![]()
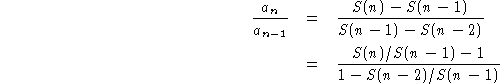
![]()
where
![]()
is a polynomial for which
![]()
(S(n),b):=GOSPER( a(n))
[assumes that a(n)/a(n-1) is a rational function,
if S(n)/S(n-1) is also a rational function then b=true
and S(n) is computed, otherwise b=false
algorithms used:
num(a) - numerator of the rational function a
den(a) - denominator of the ratinal function a
Res(x, p, q) - resultant of polynomials p, q with respect to the
variable x
gcd(p,q) - greatest common divisor of the polynomials p and q
deg(p(n)) - degree of the polynomial p(n)
coef(p(n), i) - coefficient of the ith power of n in the polynomial
p(n)]
1. b := true
2. if a(n) = 0 then S(n) := 0; return fi
3. p(n) := 1
q(n) := num(a(n) / a(n-1))
r(n) := den(a(n) / a(n-1))
4. while (Res(n, q(n), r(n+j)) has nonnegative integer root j = j0) do
g(n) := gcd(q(n), r(n+j0))
q(n) := q(n)/g(n)
r(n) := r(n)/g(n-j0)
p(n) := p(n) g(n) g(n-1) ... g(n-j0+1)
od
5. lp := deg(q(n+1) + r(n))
lm := deg(q(n+1) - r(n))
if lp <= lm then k := deg(p(n))-lm
else
k0 := 2 (-lp coef(q, lp) - coef(q, lp-1) + coef(r, lp-1))/
(coef(q, lp) + coef(r, lp))
if (k0 is integer) then k := max(k0, deg(p(n))-lp+1)
else k := deg(p(n))-lp+1
fi
fi
if k < 0 then b := false; return fi;
6. solve recurrence relation p(n)=q(n+1)f(n)-r(n)f(n-1)
with initial condition f(1)=p(1)/q(2)
for f(n)=ck n^k + ... + c0
if (solution does not exist) then b := false; return fi;
7. S(n) := q(n+1) a(n) f(n)/p(n);
return